This is the heart and soul of my practice - to teach my patients about their health, about their bodies, to best answer their unanswered questions with clarity so that they can put the knowledge into practice.
In the world of fertility, this knowledge into practice is powerful to promote (or prevent) a pregnancy. Understanding your fertility signs raises awareness of your "fertile window" and allows for an empowered action. We will dedicate the post to conception during the fertile window and dig into your 2 best fertility signs.
The fertile window is 6 days in total, give or take. It spans across the 4 days leading up to ovulation (cervical mucus is noticed, sperm can survive for approximately 5 days), ovulation day and the day after ovulation (the egg can survive 12-24 hours after ovulation).
Your best 2 fertility signs are 1) Cervical Mucous as a prediction of the start of your fertile window and approaching ovulation and 2) Ovulation confirmation via Basal Body Temperature Charting.
>>> Sign up for a Basal Body Temperature Chart & Simplified Charting Instructions HERE
1) Cervical Mucous (To Predict the Eventual Ovulation)
What: Cervical mucus changes during the menstrual cycle due to hormonal changes and it indicates fertility days and predicts ovulation. First, it can provide insights into the beginning, the peak and the end of the fertile window. Second, the cervical mucus also gives opportunity for sperm to travel up the vaginal tract and into the uterus.
How & When: As you transition from Day 1 (the first day you bleed) to mid-cycle (ovulation), the egg (and follicle) starts to grow and begins to produce estrogen. Estrogen increases in amount/potency closer to the ovulation as the follicle continues to grow, the estrogen stimulates the cervix to open up and produce more "sperm friendly" mucus.
Appearance: The cervical mucus changes from a thick, sticky mucus (at the start of the cycle = low fertility) to a thinner, slippery, and slightly stretchy mucus (closer to mid-cycle = peak/high fertility) noted it as "egg white" consistency.
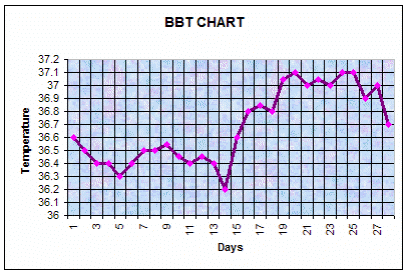
2) Ovulation via Basal Body Temperature (BBT) To Confirm Ovulation
What: Typically ovulation occurs in mid-cycle, it refers to the release of a mature egg from the ovary which travels down the Fallopian tube to the uterus, eventually. Your day of ovulation varies, it marks the 2nd last day of your fertile window with the day after ovulation being the last since the egg can last 12-24 hours. The purpose of ovulation is to allow the egg to be fertilized by the sperm, ultimately to procreate. If no fertilization takes place, the egg dies off and the cycle restarts.
When: In hormonal balance, ovulation occurs mid-cycle. For ex., in a 30 day cycle, it would occur on Day 15. However, we want to become aware of the pattern of ovulation via BBT charting as to confirm and highlight ovulation patterns.
How Temperatures Change: Estrogen dominates the first half of the cycle priming the uterus and encouraging the release of the egg from the follicle in the ovary. Estrogen is a cold hormone and temperatures are lower from Day 1 to ovulation. Progesterone dominates in the second half of the cycle and prepares the uterus for any potential implantation of a fertilized egg. Progesterone is a hot hormone and temperatures are higher after ovulation to end of cycle.
You should see a "bi-phasic pattern" - a temperature difference between your pre-ovulation (low temps) and post-ovulation (high temps) when plotted on a BBT graph. The rise in temperature is usually about 0.2-0.4 degrees Celsius, the rise is due to the corpus luteum (lining of the egg) producing progesterone (our heat-inducing hormone).
Combining Your Best Fertility Signs: The BBT can observe or confirm ovulation therefore you need to observe your cervical mucus before ovulation in order to bring awareness and prediction to your "fertile window" patterns. Recall, the fertile window are the cervical mucus days before ovulation, the day of ovulation and 12-24 hours after ovulation. Once temperatures have shifted, you are no longer in the fertile window.
Note, your BBT is your body temperature at rest in the morning after 3 hours or more of uninterrupted sleep. It needs to be taken at approximately the same time every morning. The actual temperatures are not as important as is observing a "bi-phasic pattern" showing a difference from per-ovulation to post-ovulation.
>>> Sign up for a Basal Body Temperature Chart & Simplified Charting Instructions HERE
To living in health,
Dr. Amy de Oliveira, Naturopathic Doctor
Women's & Family Natural Health Expert


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed